
Our cats are not just pets, they’re our purr-fect companions. Taking care of their well-being is in our hands. Let’s explore the art of cat food to make sure our feline friends not only have a full bowl but also lead a healthy and happy life.
Cat Food Basics
Kitty Nutrition 101
Just like us, cats need a mix of nutrients – proteins, fats, carbs, vitamins, and minerals. These are the keys to keeping your purrfect companion in top shape.
Reading Labels Like a Pro
Breaking down common ingredients in cat food is crucial for understanding the nutritional composition of your cat’s diet. The importance of high-quality protein sources and minimal fillers ensures that your cat receives a well-balanced and nutritious meal.
| Proteins | Animal Protein Sources: Chicken, turkey, beef, fish, lamb, and other meat or fish by-products.
Plant-Based Proteins: Some cat foods may include plant-based proteins like soy or pea protein. |
|---|---|
| Fats | Animal Fats: Chicken fat, fish oil, or other animal-derived fats for essential fatty acids.
Plant-Based Fats: Vegetable oils, flaxseed, or sunflower oil may contribute to a balanced fat profile. |
| Carbohydrates | Grains: Common grains include rice, corn, wheat, and oats.
Vegetables: Some cat foods incorporate vegetables like carrots or peas for added nutrients and fiber. Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, or peas might be used as carbohydrate sources. |
| Vitamins and Minerals | Vitamin Sources: Ingredients like liver or specific fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins. Mineral Sources: Bone meal, calcium carbonate, and other supplements contribute to minerals necessary for a cat's health. |
| Fillers and Binders | Grain By-Products: Corn gluten meal, wheat middlings, or other grain by-products may be used as fillers.
Cellulose: Plant fibers or cellulose derivatives may be added to provide bulk. |
| Additives and Preservatives | Antioxidants: Vitamin E or C may be used to prevent food spoilage.
Artificial Additives: Some cat foods include artificial colors, flavors, or preservatives. Natural alternatives are increasingly common. |
| Water | Moisture Content: Wet or canned cat food contains a significant amount of water, contributing to hydration. |
| Taurine | Taurine Supplement: Essential for cats, especially in commercial cat food where it may be added separately. |
| Fiber | Plant-Based Fiber: Beet pulp, chicory root, or other plant sources for digestive health. |
| Probiotics | Beneficial Bacteria: Some premium cat foods include probiotics for gut health. |
Wet vs. Dry Food
Comparing wet and dry cat food involves considering various factors, including nutritional content, convenience, cost, and the specific needs of your cat. Here’s a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed decision:
| Wet Food | Dry Food | |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Content |
Pros:
Cons:
|
Pros:
Cons:
|
| Hydration | Pros:
Cons:
| Pros:
Cons:
|
| Palatibility |
|
|
| Convenience |
|
|
| Dental Health |
|
|
| Cost |
|
|
| Special Dietery Needs |
|
|
Ingredients Matter
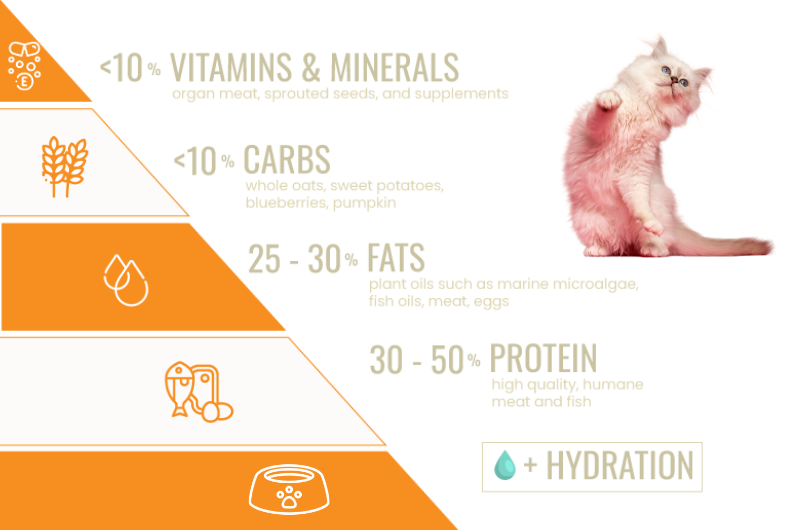
Protein Powerhouses
Ensuring optimal nutrition elements are present in your cat’s diet lays the foundation for a vibrant and active feline companion.
Fats for Furballs
Fats play a crucial role in cat food, contributing to various aspects of feline health, including a shiny coat and overall well-being. Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, in particular, are essential components that offer many benefits
Below is a breakdown of the two main groups of fatty acids that are essential for your cat’s health:
Essential Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Cats
| Function | Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA) | Supports healthy skin | Flaxseed oil, Eggs, Navy Beans |
| Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) | Helps to reduce inflammation | Fish oils, Flaxseed oil, Marine Microalgae (such as spirulina and chlorella), Sugar Kelp |
| Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) | Contributes to healthy brain development, skin, and eyes | Fish oils, Flaxseed oil, Marine Microalgae (such as spirulina and chlorella), Sugar Kelp |
| Linoleic Acid (LA) | Helps the skin retain moisture and supports healthy growth and immune function | Sunflower oil, Eggs, Sugar Kelp |
| Arachidonic Acid (AA) | Supports skin growth, reproduction, the digestive system, and blood clotting. | Fish oils, Marine Microalgae, Egg, Poultry, |
Carbs in Cat Food
Nutrient-rich carbohydrates to include in your cat’s diet:
Oats
Quinoa
Blueberries
Cranberries
Broccoli
Sweet Potato
Pumpkin
Essential Vitamins & Mineral for Cats
Here are some examples of whole foods and herbs packed with the vitamins and minerals your cat needs. Whether you’re giving air-dried, dehydrated, raw, or homemade meals, consider about adding these ingredients to your cat’s food pyramid
Essential Vitamins Cats:
| Function | Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Supports vision, teeth and bones, skin, and reproduction | Beef, Fish, Egg, Liver, Sweet Potatoes, Pumpkin, Spinach |
| Vitamin D | Supports healthy bones | Salmon, Egg, Beef Liver |
| Vitamin E | Protects cells from damage | Liver, Spinach, Sunflower Seeds |
| Vitamin K | Maintains normal blood clotting | Spinach, Broccoli |
| Thiamine | Supports carbohydrate metabolism and the nervous system | Poultry, Egg, Liver, Brewer’s Yeast |
| Riboflavin | Aids in energy | Muscle Meat, Egg, Liver Green Vegetables |
| Pantothenic Acid | Assists with maintaining a healthy metabolism | Chicken, Egg, Liver, Broccoli |
| Niacin | Maintains healthy energy and hormone production, supports metabolism, nervous system, and cognitive function | Poultry, Fish, Liver |
| Pyridoxine | Helps support a healthy metabolism | Poultry, Kidney |
| Folic Acid | Aids in the production of methionine, an essential amino acid | Liver, Kidney, Brewer’s Yeast, Green Vegetables |
| Biotin | Helps produce fatty and amino acids | Salmon, Egg, Beef Liver |
| Vitamin B12 | Supports a healthy metabolism and nervous system | Salmon, Egg, Liver, Kidney |
| Choline | Contributes to a healthy liver, nerve, and muscle function | Krill, Egg, Heart, Liver |
Essential Minerals for Cats:
| Function | Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Main mineral in healthy teeth and bones and supports normal muscle function | Salmon, Spinach, Rosemary |
| Phosphorus | Maintains healthy bones, teeth, and metabolism and helps stimulate kidney function | Chicken Liver, Brewer’s Yeast, Chervil (French Parsley) |
| Potassium | Supports nerve and muscle function | Chicken, Salmon, Dill |
| Sodium | Maintains healthy nerve and muscle cell function | Naturally occurring at various levels in meat, fruits, and vegetables |
| Chloride | Supports the metabolism and maintains healthy acid balance | Naturally occurring in many vegetables and seaweeds, like kelp |
| Magnesium | Essential mineral for healthy nerve, muscle, and heart function, supports immune health and regulates glucose | Spinach, Broccoli, Seeds |
| Iron | Maintains and supplies oxygen in the circulatory system | Beef, Poultry, Egg, Apples, Green Vegetables, Thyme |
| Copper | Aids in iron absorption and the production of bones, collagen, and tissues | Beef Liver, Spirulina, Thyme, Basil |
| Manganese | Supports the metabolism, healthy bones, and cartilage and energy production | Eggs, Green Vegetables, Thyme, Basil |
| Zinc | Promotes healthy immune and brain function, growth of skin and coat, and collagen and hormone production | Oysters, Beef Liver, Chicken Heart, Parsley |
| Iodine | Assists with hormone production in the thyroid which contributes to a healthy metabolism | Kelp |
| Selenium | Protects cells from damage and supports a healthy metabolism and thyroid | Turkey, Salmon, Beef Liver |
Understanding Cat Food Labels
Decoding Labels
Understanding common terms on cat food labels is essential for making informed choices about your feline friend’s nutrition. Here are some key terms and guidance to help you navigate cat food labels:
1. Complete and Balanced:
Definition: Indicates that the cat food provides all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions for the specific life stage as outlined by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) guidelines.
Guidance: Look for this term to ensure your cat’s diet meets their nutritional needs. Different formulas may be designed for kittens, adults, or seniors.
2. Meat By-Products:
Definition: Refers to non-muscle animal parts such as organs, blood, and bones. While controversial, high-quality by-products can contribute essential nutrients.
Guidance: Ensure the source is specified (e.g., “chicken by-products”) and that it comes from a reputable manufacturer.
3. Grain-Free:
Definition: Indicates the absence of grains like wheat, corn, and soy in the cat food.
Guidance: May be suitable for cats with grain allergies, but ensure that the food still provides a balanced nutritional profile and does not rely on excessive carbohydrates.
4. Natural or Holistic:
Definition: Suggests that the cat food contains natural ingredients without artificial additives.
Guidance: Check the ingredient list to verify the absence of artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. Be aware that these terms are not regulated.
5. Limited Ingredient Diet:
Definition: Formulated with a reduced number of ingredients, often beneficial for cats with food sensitivities or allergies.
Guidance: Check the ingredient list to identify the specific protein source and ensure it aligns with your cat’s dietary needs.
6. Grain-Inclusive:
Definition: Contains grains like rice, corn, or oats in the ingredient list.
Guidance: Suitable for cats without grain sensitivities. Ensure the grains are not excessive and are of good quality.
7. Real Meat or Meat First:
Definition: Implies that the primary protein source is meat.
Guidance: Check the ingredient list to confirm a named meat source is the first ingredient, indicating a higher-quality protein.
8. AAFCO Statement:
Definition: A statement indicating that the cat food meets the nutritional standards set by the AAFCO.
Guidance: Look for a specific life stage on the statement to match your cat’s age (e.g., “suitable for growth” for kittens).
9. Artificial Additives:
Definition: Includes artificial colors, flavors, or preservatives.
Guidance: Opt for cat foods with minimal or no artificial additives to avoid potential health issues.
10. Guaranteed Analysis:
Definition: Provides the minimum levels of crude protein and fat and the maximum levels of crude fiber and moisture.
Guidance: Use it as a general guide but remember that it doesn’t provide a complete picture of the food’s nutritional quality.
Avoiding Harmful Additives
Being aware of additives and preservatives in cat food is essential for promoting a healthier diet for your feline friend. Here’s a list of some additives and preservatives that you might want to watch out for:
BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene):
Purpose: Antioxidants to prevent fat spoilage and extend shelf life.
Concerns: Linked to potential health risks, including cancer.
Artificial Colors:
Purpose: Enhance the visual appeal of the cat food.
Concerns: Some cats may be sensitive to artificial colors, and they do not contribute to nutritional value.
Artificial Flavors:
Purpose: Enhance the taste of the cat food.
Concerns: Cats generally rely more on smell than taste; artificial flavors may not align with their preferences.
Propylene Glycol:
Purpose: Moisture retention and texture improvement.
Concerns: Potential toxicity, especially in large amounts. It is a controversial ingredient and not allowed in some countries.
Carrageenan:
Purpose: Thickening agent.
Concerns: Linked to gastrointestinal inflammation in some studies, particularly in higher concentrations.
Ethoxyquin:
Purpose: Preservative to prevent fat spoilage.
Concerns: Controversial; some studies have raised concerns about potential long-term health effects. Regulations limit its use in pet food.
Meat and Bone Meal:
Purpose: Protein source.
Concerns: Quality can vary, and it may include rendered by-products. Prefer named meat meals for better quality.
Corn Syrup:
Purpose: Sweetener and source of energy.
Concerns: High sugar content; excessive consumption may contribute to obesity and diabetes.
MSG (Monosodium Glutamate):
Purpose: Flavor enhancer.
Concerns: Some cats may be sensitive to MSG, leading to adverse reactions.
Corn, Wheat, and Soy:
Purpose: Fillers and inexpensive protein sources.
Concerns: Common allergens for cats; may contribute to digestive issues and food sensitivities.


